Thoracoscopic Management of Pleural Effusion Resulting From Peritoneal Dialysis (PD Hydrothorax) [1]
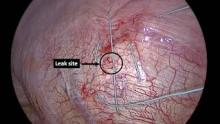
Recurrent pleural effusion secondary to peritoneal dialysis (PD hydrothorax) occurs in about 2% of patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). It can potentially be a serious problem, resulting in permanent cessation of CAPD and transition to hemodialysis. This can have many adverse consequences for some patients. Thoracic surgeons are often called upon by nephrologists for a solution to this problem.
It is thought to occur as a result of movement of peritoneal dialysate through fenestrations in the diaphragm or pleuroperitoneal communications, facilitated by the negative intrathoracic pressure. Pleural fluid analysis typically detects a higher glucose concentration than serum.
Conservative management with temporary interruption of PD has a poor success rate, whereas the efficacy of thoracoscopic intervention has been associated with success rates exceeding 90%. In this video, the authors demonstrate and discuss their approach for the thoracoscopic management of PD hydrothorax.
References
- Chow KM, Szeto CC, Li PK. Management options for hydrothorax complicating peritoneal dialysis. Semin Dial. Sep-Oct 2003;16(5):389-94. [3]
- Yaxley J, Twomey K. Peritoneal dialysis complicated by pleuroperitoneal communication and hydrothorax. Ochsner J. 2017 Spring;17(1):124–127. [4]
- Yen H-T, Lu H-Y, Liu HP, Hsieh M-J. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for hydrothorax in peritoneal dialysis patients – check-air-leakage method. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005 Oct;28(4):648-649. [5]
Disclaimer
The information and views presented on CTSNet.org represent the views of the authors and contributors of the material and not of CTSNet. Please review our full disclaimer page here [6].